 Some of Antonio Ruzzini’s PhD thesis work has been selected to be highlighted on Biochemistry’s website.
Some of Antonio Ruzzini’s PhD thesis work has been selected to be highlighted on Biochemistry’s website.
http://pubs.acs.org/journals/bichaw/index.html
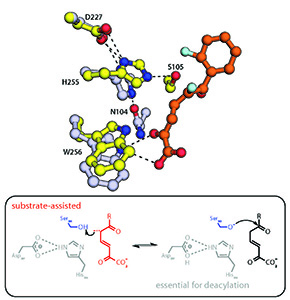
“A substrate-assisted mechanism of nucleophile activation in a Ser-His-Asp containing C-C bond hydrolase.”
Author(s): Ruzzini, Antonio; Bhowmik,Shiva; Ghosh, Subhangi; Yam, Katherine; Bolin, Jeffrey; Eltis, Lindsay
Published in American Chemical Society Journal Biochemistry. Biochemistry. 2013 52:7428-38.
Summary
Meta-Cleavage product (MCP) hydrolases are involved in the bacterial degradation of aromatic compounds and steroids: one homolog is a determinant in the degradation of PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls) while another is a potential target for novel therapeutics to treat TB. These enzymes utilize a Ser-His-Asp triad to catalyze the unusual hydrolysis of a carbon-carbon bond. In this study, we used kinetic, mutagenesis and structural approaches to demonstrate that the substrate plays a role in activating the catalytic serine for subsequent nucleophilic attack. This substrate-assisted mechanism of nucleophilic catalysis distinguishes MCP hydrolases from other serine hydrolases, and highlights the versatility of the catalytic triad.